In our daily life, thousands of elements, of which most of us are unaware of their existence and function, play a role in ensuring the perfect functioning of things in society. It cannot be denied that every time the communication networks or power goes down, what a big problem it creates. For this reason and despite the fact that technological investment in telecommunication infrastructure and power networks has made significant progress in guaranteeing services in all geographical areas, the existence of support or emergency devices is necessary to prevent damage in the event of an unexpected outage.
One of the elements we are going to talk about is UPS or emergency power supply systems, widely known as UPS (uninterruptible power supply).
UPS devices exist in places such as data centers, hospitals, office buildings, industries, transportation infrastructures such as ships, or anywhere else that requires a reliable and quality power source that is always available. They are responsible for ensuring the continuity of electricity service when the grid experiences any type of failure.
In fact, UPS is a backup so that in case of power failure, the information and services of our systems are not lost, because they are devices that can deliver electrical energy to other equipment through their UPS batteries. The energy supply time of these devices is determined according to the type and number of batteries in the system. The more UPS batteries, the more power outages we can tolerate.
Thus, a UPS ensures that, for example, the energy required by an operating room for a critical operation always remains stable. They ensure that the data centers that allow Internet connectivity to reach our homes do not shut down in the event of a power surge due to an electrical storm. Or that a ship's communication systems don't collapse due to a critical power supply failure.
UPS or uninterruptible power supply
In addition, a UPS acts as a filter for those electrical systems or devices connected to the grid. For example, if we have one of these uninterruptible power supply systems, we protect all computer equipment from possible fluctuations or voltage peaks, interference, frequency changes or small interruptions. The UPS function filters out all of these. Therefore, it guarantees both the proper operation of the equipment connected to the network and its lifespan.
How does an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) work?
To better understand how these elements work, it is first necessary to know what components the UPS consists of.
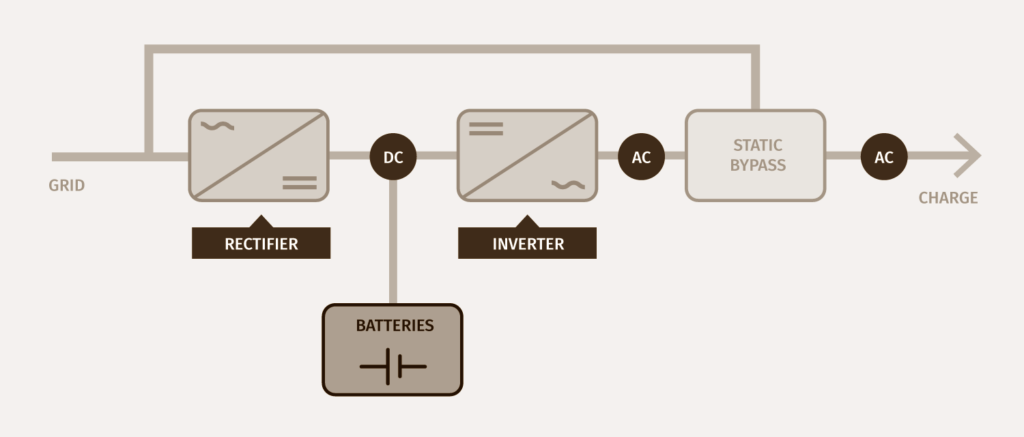
Rectifier/charger: It is responsible for converting the alternating current that enters through the network into direct current or for charging batteries or feeding the inverter.
UPS battery: provides the electrical energy needed to feed the system in case of power failure.
Inverter: Converts the electrical current coming from the rectifier or batteries from direct current to alternating current to be distributed to the systems connected to the UPS.
Static bypass and maintenance: This type of electrical circuit allows the electrical charge to be connected directly to the main network (or a separate network) in the event of a UPS fault.
Control unit: It is an intelligent element that the uninterruptible power supply system is equipped with. which, depending on the type of UPS device and its function, enables a series of functions through software or other items.
How will its normal function be?
When the UPS is operating normally, i.e. from an available and quality source, power is supplied to the grid through the UPS connection. In the first stage, it passes through the rectifier, which converts the electricity from alternating current to direct current.
This conversion is necessary because part of the electricity must be stored in the battery - where the current must be direct current - and the rest of the electricity continues its way to the inverter, turning it back into alternating current to power the connected systems.
What happens if there is a power outage?
Imagine that the grid is no longer available or the voltage is not within the allowed quality range, in this case the inverter is powered by the DC voltage provided by the UPS battery. The output of the inverter remains unchanged and therefore the electrical load connected to the system continues to work without interruption.
The time the batteries can supply the system depends on the required consumption of the equipment as well as the capacity of the UPS battery. When the main supply voltage is restored, i.e. reaches a value within the allowed tolerances, the rectifier resumes operation and normal operation is restored.
Batteries that have been discharged during a power outage are recovered by being recharged through the DC voltage supplied by the rectifier/charger.
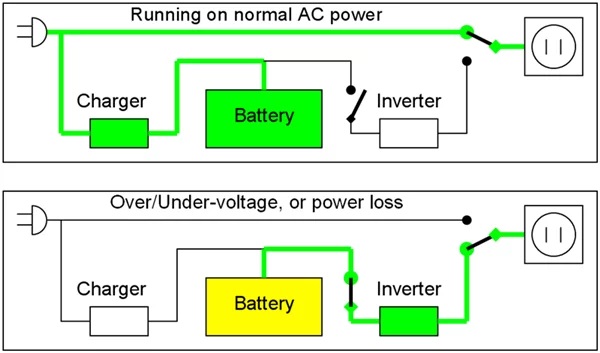
What should we do if there is a fault in the UPS or we need to do maintenance work?
In the event of a fault in the UPS, the static bypass is automatically activated and immediately transfers the electrical charge to the main supply network (or bypass) in the event of an overload or short circuit. So, whatever the operation, the UPS ensures that there is no interruption in the power supply.






 تیتر مطلب در این قسمت نمایش داده می شود تیتر مطلب
تیتر مطلب در این قسمت نمایش داده می شود تیتر مطلب